Pig Butchering Scam

The pig butchering scam is a devastating fraud that combines emotional manipulation with financial deceit, costing victims billions annually. Named after the practice of fattening pigs before slaughter, scammers build trust over time before stealing money through fake investment schemes, often involving cryptocurrency. This article explores the pig butchering scam meaning, its mechanics, impact, and how to stay safe.
What Is the Pig Butchering Scam?
The pig butchering scam is a long-term fraud where scammers pose as friendly or romantic contacts to trick victims into investing in fake opportunities. Originating in China around 2016, it’s called “Sha Zhu Pan” and has grown globally, often tied to organized crime. Scammers use social media, dating apps, or texts to start conversations, spending weeks or months gaining trust before introducing fraudulent investments.
Victims are led to believe they’re earning profits, but their money is stolen. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reports that these scams exploit trust and technology, making them hard to detect. Awareness is key to avoiding this growing threat.
Origins and History
The pig butchering scam began in China, targeting gamblers and dating site users, but has since spread worldwide. By 2020, it reached the U.S., fueled by cryptocurrency’s rise and organized crime networks, often in Southeast Asia. The United Nations notes that scam operations in places like Myanmar use trafficked workers forced to deceive victims.
In 2024, the scam evolved with AI tools like deepfakes, making fraudsters seem more credible. The U.S. Department of Justice has linked these scams to billions in losses, highlighting their global impact. The scam’s growth shows the need for stronger international cooperation.
How the Pig Butchering Scam Works
Scammers start with a simple message on platforms like Facebook or WhatsApp, often pretending to be a romantic interest or friend. They build trust over months, sharing fake stories of wealth to seem successful. Eventually, they introduce the pig butchering scam crypto scheme, guiding victims to buy cryptocurrency on legitimate exchanges.
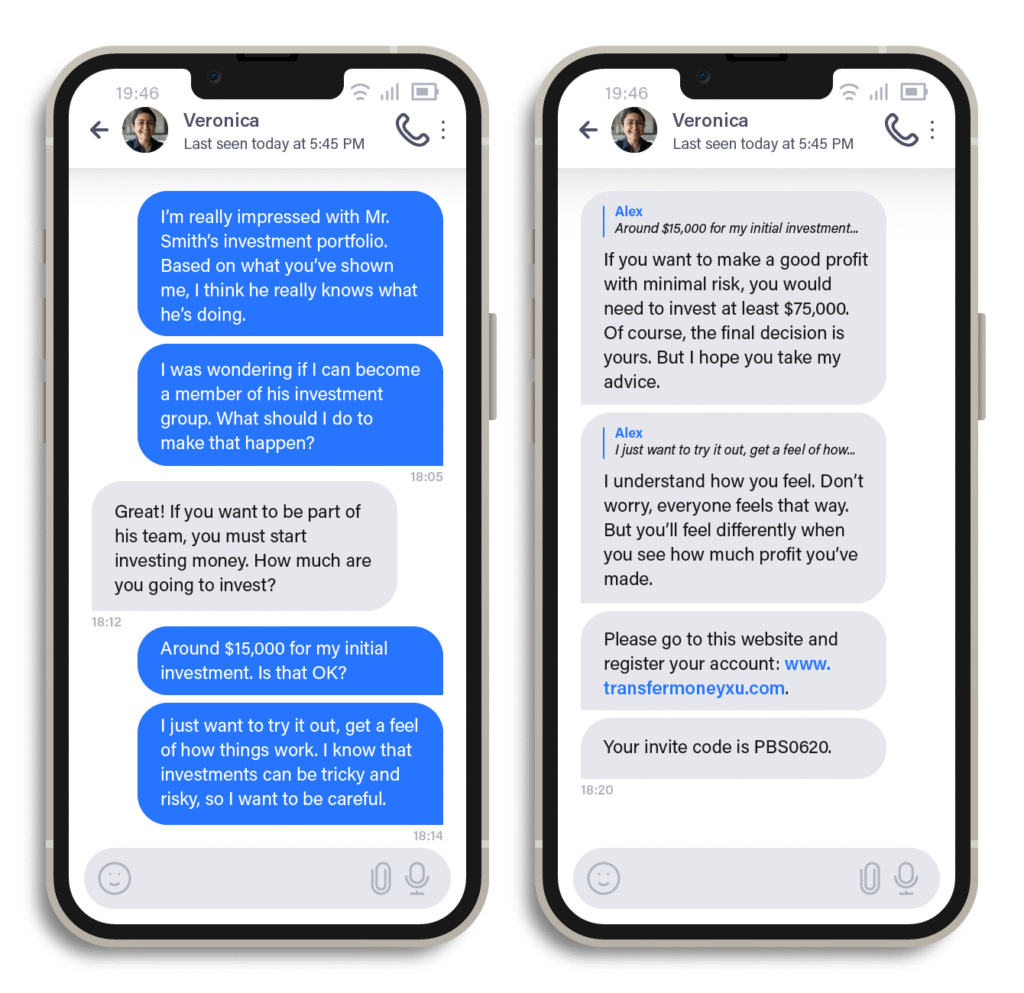
Victims then transfer funds to fake platforms that mimic real trading sites, showing false profits. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) warns that these platforms block withdrawals, demanding more money for “fees” or “taxes.” Scammers vanish, leaving victims with nothing.
Common Tactics and Red Flags
Scammers use emotional manipulation, posing as romantic partners or mentors, and create urgency to invest quickly. They may use AI-generated voices or videos to seem real. Fake websites and apps, sometimes found on app stores, show artificial gains to lure more deposits.
The FBI lists red flags: unsolicited investment offers, guaranteed high returns, and pressure to act fast. Always verify platforms with trusted sources like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Be cautious of anyone avoiding in-person meetings or pushing crypto investments.
Key Red Flags of Pig Butchering Scams
- Unsolicited messages from strangers offering investment tips.
- Promises of quick, high returns with no risk.
- Fake platforms showing artificial profits.
- Demands for additional fees to withdraw funds.
Pig Butchering Scam Stories
Real-life pig butchering scam stories show the scam’s emotional and financial toll. Shai Plonski, a California resident, lost his life savings after a “romantic” contact on Facebook convinced him to invest in crypto. He was shown fake profits but couldn’t withdraw his money, as reported by ABC News.
Barry May, a retiree, lost $500,000 after a scammer promised marriage and wealth. The FBI intervened before he took a loan, but most of his savings were gone. These stories, shared by the FBI, highlight the need for vigilance.
Impact and Statistics
The pig butchering scam has caused massive losses, with $9.9 billion stolen globally in 2024, per Chainalysis. In the U.S., the FBI reported $5.8 billion in investment fraud losses, with 18,000 crypto scam complaints in the first half of 2024. Seniors are especially vulnerable, losing $4.9 billion.
Beyond finances, victims face shame and emotional distress. The scam’s ties to human trafficking, as noted by the United Nations, add a darker layer, with workers forced to run scams. This global crisis demands urgent action.
2024 Pig Butchering Scam Statistics
| Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Global Losses | $9.9 billion (Chainalysis) |
| U.S. Investment Fraud Losses | $5.8 billion (FBI) |
| Crypto Scam Complaints (U.S.) | 18,000 in first half of 2024 |
| Senior Losses | $4.9 billion |
Pig Butchering Scam News
Recent pig butchering scam news shows law enforcement fighting back. The FBI’s Operation Level Up notified 4,300 victims in 2024, saving $285 million, as reported by Nextgov. The U.S. Department of Justice seized $225 million in crypto linked to these scams, a record amount.
Despite successes, scammers operate overseas, making prosecution hard. The FBI urges reporting to track funds via blockchain. Public awareness campaigns are growing to combat this fast-spreading crime.
Pig Butchering Scam FBI Efforts
The pig butchering scam FBI response includes proactive measures. The FBI’s Operation Level Up uses blockchain analysis to trace funds and warn victims. In 2024, agents contacted thousands, preventing further losses. The FBI’s IC3 encourages reporting with details like wallet addresses and transaction IDs.
The FBI works with exchanges and social media platforms to identify scammers, often linked to Chinese crime groups. While recovery is rare, seizures like the $8.2 million in 2024 show progress. Reporting quickly is critical for any chance of recovery.
Prevention and Protection Strategies
To avoid the pig butchering scam, verify all investment opportunities. Check platforms with the SEC and avoid sharing personal details with strangers online. Use two-factor authentication on crypto wallets, as advised by FinCEN.
Be skeptical of high-return promises and consult financial advisors. Community efforts, like FBI warnings, and policy actions, such as U.S. Treasury sanctions, aim to disrupt scam networks. Education is your best defense.
Reporting and Recovery
If you suspect a scam, report it immediately to the FBI’s IC3. Provide scammer details, website URLs, screenshots, and transaction records (e.g., “12/22/24 – Sent 0.5 ETH to 0x…”). Recovery is difficult due to blockchain’s irreversible nature, but the FBI recovered $140,000 in one 2024 case.
Support resources include local police and counseling for emotional recovery. The FTC offers scam prevention tips. Quick reporting can help authorities track and stop scammers.
Conclusion
The pig butchering scam is a cruel blend of emotional and financial fraud, exploiting trust to steal billions. By understanding its tactics, recognizing red flags, and reporting promptly, you can protect yourself. Stay informed, share knowledge, and help fight this global threat.
- GMT
- OTL
- ICL
- GMF
- FYE
- DTN
- UWU
- TT
- CFS
- BD
- NTM
- WUT
- MIL
- TMRW
- BG
- FWU
- TTYL
- WYFD
- WSG
- ETA Meaning
- AFK Meaning
- BRB
- OP
- Buff
- LMS
- ATP
- WTV
- ML
- IGH Meaning
- IMS
- LYK
- PTSO Meaning
- LTR
- NS
- Grool Meaning
- TMB
- PNP
- EDTWT
- WYLL
- CM Meaning
- Passenger Princess Meaning
- RQ Meaning
- BFFR Meaning
- NTY Meaning
- DTM Meaning
- LBVS Meaning
- FRL Meaning
- OTW
- WTW
- IMBO
- LCOL Meaning
- VHCOL Meaning
- Face Card Never Declines
- 4L Meaning
- Pink Person Meaning
- Blue Person Meaning
- Green Person Meaning
- FYM Meaning
- GL Meaning
- HCOL Meaning
- A Guide to Internet Slang for Jokes and Playful Teasing
- HU Meaning in Text
- CBFW Meaning
- Mullet
- Da Fuq Meaning
- WTF Meaning
- What Is Glazing Slang
- MCOL Meaning
- YWA Meaning
- FWM Meaning in Text
- What Does QQIA Stand For
- What Does LGBTI Stands For
- What Does GSD Stands For
- What Does LGBT2Q Stands For
- What Is Yaoi and BL
- Josou Seme
- Juevos
- Paizuri Meaning
- Corruption Kink
- Cockwarming Meaning
- Torpedophile
- Fap Chat
- Wassach
- Cockhair
- BUHB
- IDTS Meaning in Text
- Kest Gak
- r Bonersinpublic
- Pararam Tram
- TTM and TWM
- BBL
- Wanktube
- Time Stophentai
- Gripster
- HBY Meaning in Text
- Shook Meaning
- GG Meaning
- GOAT Meaning
- Bussin Meaning
- MBN
- FMTY Meaning
- AMOS
- What Is Rule 34
- Amongus R34
- Whats Up Chicken Butt
- Fangdangler
- Exposed Faggot and Exposed Fags
- TN Meaning
- HY
- Sneaky Links
- Memable
- What Does PMO Mean in Text
- How Accurate Are Love Calculators
- History of Love Calculators
- Love Calculators vs Astrology
- What Does LGBTQCIA Stand For
- TS
- HBU
- OOC Meaning
- Soft Launch
- Sneak Peeks
- Seggs
- Kenough
- IYKYK
- Facial Recognition in the Crypto Apps
- SFW
- What Is Broheim
- Synthetic Identity Fraud
- How to Choose the Right Insurance A Detailed Guide
- How to Choose the Right Doctor
- Essential Services Needed When Building or Repairing a House
- Slangs Terms in the Fashion Industry
- Kokushibo R34
- Intravert Meaning
- KGFE
- Rock God
- TW Meaning
- IKTR Meaning
- ILYK Meaning
- Oomfie Meaning
- What Does ND Meaning in Text
- What Does WAP Stand For
- B G Meaning
- ASF
- Allat Meaning
- Country Humans R34
- Widepeepohappy
- ODAAT Meaning
- Skyrocket Your Career Skills Refined by a Brisbane Business Coach
- R34 Toy Chica
- Upgrade Backyard with Smart Building Strategies
- Best Practices for Using Storage Tanks
- Product Liability Laws
- Nail Health Matters Effective Solutions for Managing Fungal Infections
- Outta Pocket Meaning
- Home Office Space
- Essential Techniques for Product Transport
- PU Meaning in Text
- What Is r Traps or Traps
- W R T Meaning
- How Technology Has Changed Business
- Adding Dedicated Web Hosting to Your Hosting as a Partner
- GGS Meaning
- Digital Marketing is Influencing Crypto Industry
- TradeFolder Review
- Your Ultimate Guide to Party Planning A Comprehensive Checklist
- SMTH Meaning
- Maximizing Your Returns The Importance of Strategic Tax Planning
- From Slang to Slots
- JP
- FN Meaning
- Skullet
- How to Obtain a Medical Prescription to Purchase a Disposable THC Vape
- Sprinkle Sprinkle Meaning
- The Essential GTM Guide Strategies for Success from Product Marketing Experts
- Are Yacht Rentals Worth the Investment for Corporate Retreats
- 4 Must Know Insights for Every Entry Level Developer on API Testing
- Fruity Fragrance of Pineapple
- The Ultimate Guide to Apartments for Seniors Finding Your Ideal Home
- Dog in Him
- I Got That Dog in Me
- Financial Mastery with the Investment Handbook
- XX Meaning in Text
- Unlock Homeownership with a Free ITIN Loan Quote Fast Efficient and Designed for You
- XD
- How to Edit a JPEG Like a Pro Step by Step Tutorial
- Meaning of TG
- WYMM Meaning in Text
- Caught in 4K
- SOS Meaning
- Productive Day
- Tweakin Meaning
- Unveiling the Power of IRA Investing
- What to Look for in a Law Firm SEO Expert
- CTFU
- Boba Tea Near Me Tips to Find Nearby Bubble Tea Spots
- S U Meaning
- What Does ISO Mean on Social Media and Texting
- H T
- The Crucial Role of Financing in Real Estate Development
- AWL Meaning in Text
- Live Webinar ClickMeeting Promoting Your Webinar Effectively
- Pawns App Is It a Legitimate Website for Online Surveys
- What Does NTN Mean in Text
- Caribbean Yacht Charters
- Meaning of Dropping Dimes
- What Does Stimmy Check Mean
- Retail ERP Software
- Big Sized Disciple
- The Role of Forensic Accountants in High Net Worth Divorces in Florida
- The Importance of Hiring an Estate Planning Attorney
- Brand Promotions
- Mar1uhh
- What Does WBU Mean
- Basic Arabic Slang for Talking with Arabs
- Gamers Slang
- What Is PVC Welding
- All About Printing Equipments
- The Contribution of Technology to the Growth of Situs Toto Platforms
- 5 Factors to Consider When Selecting an Investigative Agency to Handle Your Fraud Case
- How to Choose the Perfect Perfume Oil for Every Occasion
- Goated with the Sauce
- Chromer
- What Is Pager
- DiamondWhale Review
- Top 10 Business Ideas to Consider in European Countries
- Disposal Services Small Businesses
- Camwhor Meaning
- Noble Steed
- Smoke and a Pancake
- Comf
- How Robotics and Automation Are Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management
- TheJavaSea Me Leaks AIO TLP
- Biguns Meaning
- How to Gather Google Reviews for a Senior Citizen Center
- Why Choose an Online IOP for Your Mental Health Needs
- Jordan Shoes
- What Is Frave
- Necktie Design
- Email Campaign Management
- Long Term Pest Control
- How Can Businesses Best Leverage Artificial Intelligence
- 6 AI Influenced Business Trends Everyone Must Anticipate in 2025
- PAWG Meaning
- 5 Ways Financing to Plan the Wedding of Your Dreams
- Use a White Neon Sign for a Clean and Chic Look
- The Benefits of Cloud Faxing for Modern Businesses
- BBW Meaning
- GYAT
- Top Graphic Design Firms
- No Diddy Meaning
- Helping High School Students Set Realistic Goals for the Future
- Building Connections with Online Gaming Communities
- What Does Goon Caption Means
- Secrets That Your Blackjack Dealer Doesn't Want You to Know
- Insurance BPO
- What Is Incestables
- Online Visibility
- What Is Lumpty
- Sloppy Looking Means
- Young Couples
- Hafa Adai Meaning
- 448 Angel Number
- Maximize Performance on a Budget Friendly Hosting Plan
- 5 Casino Software Developers the United Kingdom is Known For
- Tuggie
- Snuffies
- Electric Bike
- Botulax 100 Units Achieving Optimal Results with Botulinum Toxin
- Class Action Attorneys
- YOLO
- ONG
- TBH
- WFA
- Lifestyle Adjustments That Can Improve Your Vision Health
- Easy Tips to Choose the Best Online Slot for Your Play Style
- The Psychology Behind Winning at Casino Games
- How Recent Tech Advancements Might Affect the Future of Crypto
- Finished Slangily
- What Does NFS Mean on IG
- What Types of Slang Are There in Different Types of Online Games
- FPPD Meaning
- HDBD Meaning
- Gaming The Ultimate Stress Busting Hobby
- Why Jiu Jitsu is a Proven Martial Art for Effective Self Defense Preparedness
- Commercial Warehouse for Rent
- Why Casino Gaming Sites Are a Favorite for Everyone
- Instagram Story Viewer for Privacy Conscious Users to View IG Profiles
- Earring Trends Whats Hot Right Now in 2024
- CNAT Meaning
- Is Digital Marketing a Bubble or a Stable Business
- WYF Meaning
- Boston Car Service for Executive Transfers to Meetings and Events
- Arrive in Style for Your Prom Night with Car Service San Diego
- Limo Service San Diego Helps You Impress at Business Meetings
- Black Limo Service Seattle for Tips for Wedding Transportation
- The Best Features of Limo Service Connecticut for Wedding Transport
- Key Property Details Explained by Home Inspectors Fort Myers
- Moose Knuckle Meaning
- Urban Clothing Apparel
- GITSS Meaning
- Whats the Right Addiction Treatment for You Find Out Now
- Common Scientific Calculator Mistakes Avoid These Pitfalls
- The Benefits of Evaporative Cooling Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
- How to Style Your Netball Shorts for Both Practice and Casual Wear
- Understanding the Property Market Trends and Forecasts
- Alternative Investments in Australia Options Beyond Traditional Assets
- Key Considerations When Choosing a Commercial Buyers Agent
- Casualness Delight
- How Do Football Clubs Manage Star Players
- YK Meaning
- KEKL Meaning
- What to Look for in an Everyday Bra
- How to Raise Your Online Lottery Probabilities of Winning
- Every Door Direct Mail
- What Is Spankbang
- NOTAFLOF Meaning
- Energy Optimization
- Edibles Online
- OTD Meaning
- Botox in Jaw for TMJ
- Buying a Sea View Villa in Dubai for Investment
- DK Meaning
- Professional Documents
- What Does PSE Mean
- CLB Meaning
- Mayan Tomb Uncover Hidden Treasures in the Heart of the Jungle
- SEO Agency in Dubai
- Top 10 Amenities to Look for in Budget Motels
- GTK Meaning
- Liability Lawyers
- What Does Blud Mean
- Partition Actions
- Laser Cutting Steel
- Charcuterie Board Catering
- Western Boots
- Affordable Self Storage
- What Does Hmph Mean
- What Does Feeling Froggy Mean
- How Can Digital Marketing Services Help You Find a Kratom Shop in Phoenix
- How to Manage Pre Exam Nerves for the DAT
- Camcrush Meaning
- Download TikTok and Twitter Videos with SSSTik
- Financial Steps to Follow When Relocating from Germany
- Popular Entertainment Franchises for Launching a Successful Business
- What Does So Retro Mean
- Cycling Certification
- Crotch Rope
- Why Debt Funds Are Essential for Risk Management
- Goose Decoy
- Psychology Behind Humans Adoring Superheroes
- What Does Art of Zoo Mean
- Meaning of SMIRF
- 5 Ways Bed Pads Can Improve Comfort for Adults
- How to Sign a Proposal Online
- Old Mother
- Car Crash Attorneys
- Dental Advertisement
- Advanced Baccarat Player Betting Strategies to Get High Returns
- What Does A Band Money Mean
- How Do Apparel Fulfilment Services Integrate with E Commerce Platforms A Comprehensive Guide
- Optimizing Daily Workflows with Online Task Management Solutions
- LOML Meaning
- OIY Meaning
- SP Meaning in Text
- Exploring the Allure of Popular Themed Online Slot Games
- Cheap Loan with Low Interest Rates
- The Role of AI in Healthcare ChatGPTs Potential Within HIPAA Guidelines
- Shilajit in the UK Discover the Benefits of This Ancient Superfood
- How Payout Percentages Influence Online Slot Jackpot Wins
- Simplify Your International Journey How to Get an Apostille Effectively
- Funcle Meaning
- Xiao R34
- A Beginners Guide to Online Shopping Safe Payment Practices
- Best Pistols
- Deck Boots
- The Use of BiPAP and VPAP in the Treatment of Sleep Apnea What Are the Advantages of Modern Technologies
- How to Choose the Right Kurkuma for Your Needs
- WDYLL Meaning
- Top Ways to Unwind and Relax Online After a Busy Day
- How to Discuss Your Hepatitis C Treatment Plan with Your Doctor
- Wrongful Dismissal Lawyer
- Car Accident Lawsuit Process
- Working Capital Fund
- Small Apartment Complex
- Ideas for Fitness
- Studio House
- Duplex High Rise Apartment
- Apartment Gym Workout
- 4 Bedroom Apartment
- What Does YNS Mean in Slang
- What Does Chupapi Munyayo Mean
- Three Bedroom
- Study Areas
- 7 Ways to Look for Top Quality Kratom Drinks During Cyber Monday Offers
- What Does Fujitsu Mid Tier SEER Rating Mean
- What Does Ground Time Mean
- Bone Graft Material
- Liquid Cooled Generator
- How Can You Maximize Compensation After a Car Accident in Queens Expert Tips and Strategies
- Why Invest in Maid Services for a Cleaner Healthier Home Environment
- What Does Meaning With Trailer Mean With Perm
- What Is a Casino VIP and How Do You Become One
- Unraveling Esports Betting From Its Evolution to Winning Tips
- What Does NAKT Mean
- What Does Nice Try Diddy Mean on Instagram
- Gated Community Homes for Rent
- What Does OV Hoe Mean
- How Herbal Remedies Are Making Their Way Into Smoothies and Teas
- How to Unlock Savings with Canada Kratom Express Coupons
- Mini Excavator in Australia
- 7 Diet Additions You Should Invest in Today
- What Features Matter Most in a Small TV
- Telehealth GPS Explained What to Expect From Online Doctor Visits
- Applied Health Science Degree in Dermal Therapy
- What Does Previewing on the Seestar S50 Mean
- What Does SPWM Mean in Text
- How Art Elevated Online Slots
- What Does The Mans Scope Mean
- What Does The Name Xyonna Mean
- Professional Insurance Services
- What Is The Meaning of Gantos Axe
- What Does 69 Ms Mean for Latency
- How Can Businesses Optimize Costs With Mobile Solutions in Jamaica
- Seasoning Blend
- Meaning of FKH
- GTS Meaning
- What Does Hmmm Mean From a Guy Flirty
- Best Ways to Keep Your Hair Healthy and Shiny Expert Tips and Tricks
- What Does Samba Mean in Tshiluba English
- What Does IMK Mean in Texting
- Boob Job Recovery
- Dream Living Room
- Motorcycle Accident
- What Does GGE Mean Slang
- NFS Mean on Wizz
- Payment Processed
- How Slot Games Are Made Learn About Game Development
- What Does Dac Biet Mean
- Comprehensive Pearland Plumbing Services for Your Home and Business
